Last updated on March 12, 2025
Phishing-resistant MFA is the future of cyber security. So, learning about the differences between standard multi-factor authentication and phishing-resistant MFA is essential for your security. Read this post to learn about the differences between Phishing-Resistant MFA vs. Standard MFA.
Secure Phishing-Resistant MFA
Cutting-edge phishing-resistant multi-factor authentication using FIDO2 & FIDO U2F security keys and hardware & software passkeys. Interested? Try Rublon MFA for 30 days for free and see how simple it is.
Standard MFA vs. Phishing-Resistant MFA: What’s the Difference?
The main difference between phishing-resistant MFA and standard MFA is that standard MFA does not protect from phishing attacks, while phishing-resistant MFA does. Phishing-resistant MFA uses secure, unphishable authentication methods like FIDO security keys, whereas standard MFA typically relies on methods like OTP codes or push notifications, which are vulnerable to phishing.
What is Standard MFA?
Standard Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds a second layer of security beyond a password by requiring users to authenticate with something they have or something they are. However, standard MFA uses methods that are still vulnerable to attacks like phishing, where attackers trick users into revealing their passwords and codes. In addition, standard MFA can be susceptible to other cyberattacks, such as SIM swapping and push bombing. Despite offering superior account protection relative to passwords, standard MFA still exposes users to risks, especially in high-security environments.
Standard MFA is not enough. Try phishing-resistant MFA now →
What is Phishing-Resistant MFA?
Phishing-resistant MFA is a type of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) that uses secure authentication methods that attackers cannot intercept or phish. Examples of such methods include FIDO2 security keys and Passkeys. These methods create a unique cryptographic relationship between the user’s device and the service they are accessing. This ensures that login credentials are never shared or exposed to attacks. Phishing-resistant multi-factor authentication is not vulnerable to phishing, SIM swapping, and push bombing attacks. For that reason, it is more secure than standard MFA.
Standard MFA vs. Phishing-Resistant MFA: Differences Table
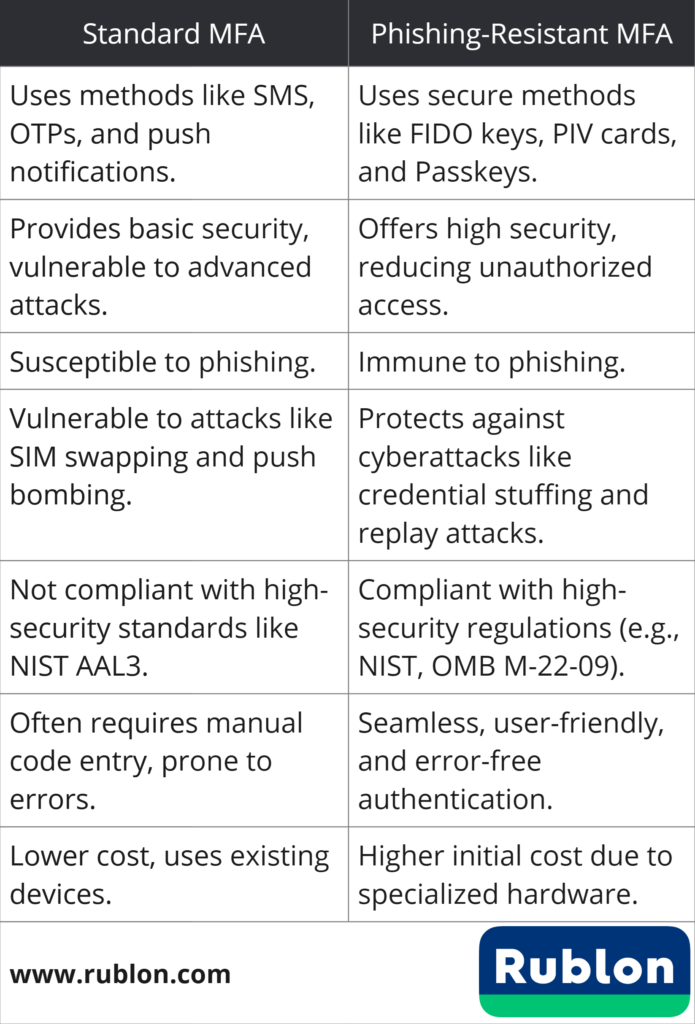
| Standard MFA | Phishing-Resistant MFA |
| Standard MFA encompasses authentication methods such as SMS codes, OTPs, push notifications, etc. | Phishing-resistant MFA includes secure authentication methods like FIDO security keys, PIV cards, and Passkeys. |
| Standard MFA provides a basic level of security but can be compromised by sophisticated attacks | Phishing-resistant MFA offers a higher level of security assurance, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access. |
| Standard MFA is susceptible to phishing. | Phishing-resistant MFA is immune to phishing. |
| Standard MFA is vulnerable to cyberattacks like SIM swapping and push bombing, depending on the authentication method used. | Phishing-resistant MFA protects against many types of cyberattacks like credential stuffing and replay attacks. |
| Standard MFA is not compliant with high-security requirements like NIST SP 800-63B AAL3, the highest level of NIST assurance for digital authentication methods. | Phishing-resistant MFA is compliant with high-security regulations like OMB Memo M-22-09 Federal Zero Trust Strategy, which specifically details how federal agencies should adopt phishing-resistant MFA. |
| Standard MFA often requires users to enter codes manually, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors. | Phishing-resistant MFA involves simpler, more seamless authentication processes, such as tapping a security key. |
| Standard MFA is usually lower in cost because it can utilize existing devices. | Phishing-resistant MFA is usually expensive because most contemporary implementations require specialized hardware like FIDO security keys or PIV card readers. |
Don’t Have Phishing-Resistant MFA Yet?
You should. Google hasn’t udergone a successful phishing attack since 2017 when they introduced FIDO security keys for over 85,000 employees. The trade-off is worth it. Start your Free Trial of phishing-resistant MFA and see for yourself the difference it makes.
Advantages of Phishing-Resistant MFA Over Standard MFA
Here’s why phishing-resistant MFA is better than traditional MFA:
- Phishing-resistant MFA is more compliant: Due to the vulnerabilities of standard MFA, regulatory bodies increasingly mandate or recommend phishing-resistant MFA. This is especially true for high-risk industries like healthcare and government.
- Phishing-resistant MFA is more secure: Phishing-resistant multi-factor authentication removes elements vulnerable to phishing. For example, SMS codes and OTPs, which can be intercepted or stolen.
- Phishing-resistant MFA is phishing-proof: Methods such as FIDO2 security keys and Passkeys use cryptographic signatures and domain binding. This ensures attackers cannot phish or intercept credentials.
- Phishing-resistant MFA is tamper-proof: Phishing-resistant MFA offers strong tamper resistance by securely storing cryptographic keys in physical devices. This makes the keys highly resistant to modification or extraction.
Phishing-Resistant vs. Standard MFA: Real-World Case Studies
While standard multi-factor authentication (MFA) enhances security beyond simple passwords, it remains susceptible to sophisticated attacks such as MFA fatigue and MFA bombing. These methods exploit user behavior and system vulnerabilities, leading to unauthorized access despite MFA implementation.
Case Study: The Apple MFA Fatigue Attack
In March 2024, Apple users were targeted in a sophisticated multi-factor authentication (MFA) fatigue attack. Attackers exploited a vulnerability in Apple’s password reset system, allowing them to inundate users’ devices with repeated password reset notifications. This relentless barrage aimed to frustrate users into inadvertently approving unauthorized access requests. In some instances, attackers followed up with phone calls spoofing Apple’s support number, attempting to extract one-time passcodes from victims. This incident underscores the critical need for organizations to implement phishing-resistant MFA solutions to safeguard user accounts against such persistent threats.
Case Study: The Uber Breach
In 2022, Uber experienced a significant security breach attributed to an MFA fatigue attack. Attackers inundated an employee with repeated MFA push notifications, eventually leading the individual to approve one inadvertently. This unauthorized access compromised sensitive company data, highlighting the limitations of standard MFA methods against persistent threats.
Case Study: Microsoft Office 365 Phishing Campaign
A widespread phishing campaign targeted Microsoft Office 365 users by circumventing standard MFA protocols. Attackers employed deceptive tactics to trick users into providing authentication codes, thereby gaining unauthorized access to accounts. This incident underscores the necessity for more robust, phishing-resistant MFA solutions.
Which Industry Standards Favor Phishing-Resistant MFA Over Standard MFA
The evolving cybersecurity landscape has prompted regulatory bodies to mandate stronger authentication measures, including phishing-resistant MFA.
OMB Memorandum M-22-09
The U.S. Office of Management and Budget’s Memorandum M-22-09 requires federal agencies to implement phishing-resistant MFA as part of a broader zero-trust cybersecurity strategy. This mandate underscores the federal government’s commitment to enhancing security protocols across its agencies. As of 2025, this requirement remains in effect, reflecting a sustained emphasis on robust cybersecurity measures.
NIST Special Publication 800-63B
The National Institute of Standards and Technology’s Special Publication 800-63B outlines digital identity guidelines, specifying that Authentication Assurance Level 3 (AAL3) requires phishing-resistant authentication methods. This standard is a benchmark for organizations aiming to achieve high-security assurance in their authentication processes.
NIS2 Directive
The European Union’s Network and Information Security Directive 2 (NIS2) aims to enhance cybersecurity resilience across member states. While NIS2 does not explicitly mandate phishing-resistant multi-factor authentication (MFA), it emphasizes the implementation of robust security measures to protect critical infrastructure and supply chains.
Article 21 of the NIS2 Directive outlines minimum security requirements, including the use of MFA or continuous authentication solutions where appropriate. Implementing phishing-resistant MFA can significantly bolster defenses against sophisticated cyber threats, thereby aligning with NIS2’s objectives. Organizations seeking to comply with NIS2 can benefit from adopting phishing-resistant MFA to protect their supply chains.
European Union’s PSD2
The European Union’s Revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2) mandates strong customer authentication for electronic payments, effectively requiring MFA. While not explicitly termed “phishing-resistant,” the directive emphasizes the need for robust authentication mechanisms to protect consumer transactions.
Navigating the Transition: Overcoming Challenges in Moving from Standard to Phishing-Resistant MFA
Transitioning to phishing-resistant MFA presents several challenges, particularly concerning user experience and cost.
Cost of Hardware Security Keys
Implementing hardware-based solutions, such as phishing-resistant FIDO security keys, can be cost-prohibitive for some organizations. These physical tokens require investment in the devices themselves and the infrastructure to support their deployment and management. One way of mitigating costs is finding an MFA provider that integrates the FIDO standard into its MFA platform and offers a variety of FIDO security keys for purchase.
Phishing-resistant Rublon MFA with FIDO security keys – Start Now →
Software-Based Passkeys as Alternatives
To mitigate costs, organizations can consider using software-based passkeys instead of hardware-based passkeys, Software passkeys utilize cryptographic credentials stored securely on users’ devices. These passkeys can be stored on computers or mobile phones, leveraging existing hardware to provide secure authentication without the need for additional physical tokens. This approach offers a cost-effective alternative while maintaining a high level of security.
Balancing Security and Usability
Ensuring a seamless user experience is crucial for the successful adoption of new security measures. Organizations must provide adequate training and support to facilitate the transition to phishing-resistant MFA, addressing potential user resistance and technical challenges.
Replacing Traditional MFA With Phishing-Resistant MFA: Cost-Benefit Analysis
Evaluating the financial implications of adopting phishing-resistant MFA involves considering both the upfront costs and the potential savings from mitigating security breaches.
Upfront Costs
- Hardware Tokens: Purchasing FIDO security keys or similar devices entails direct expenses, which can be substantial depending on the organization’s size.
- Implementation: Integrating new authentication methods into existing systems may require additional resources and training.
Potential Savings
- Operational Efficiency: Enhanced security measures can lead to streamlined access controls and reduced administrative overhead in managing security incidents.
- Reduced Breach Costs: Implementing phishing-resistant MFA can significantly lower the risk of a successful security compromise, thereby avoiding costs associated with data breaches, including legal fees, regulatory fines, and reputational damage.
Enable Phishing-Resistant MFA for Workforce Logins
Rublon MFA via phishing-resistant methods like FIDO security keys and Passkeys offers unparalleled protection and a robust security posture. Experience cutting-edge cyber security for your workforce, with seamless integration and zero hassle.
Get a Free 30-Day Rublon MFA Trial and experience the benefits of next-level multi-factor authentication today.